But anyway... fungus could be the source of the next or a future pandemic, and it would be catastrophic.
Thanks for tuning in.
https://futurism.com/neoscope/next-pandemic-fungi-scientists-warn
8. 11. 22 / BY VICTOR TANGERMANN
Disease experts are worrying that the next pandemic could be caused by fungi rather than a virus, National Geographic reports — a terrifying possibility, scientists say, given how little we know about the organisms.
Many fungi have been known to grow resistant to treatments, heightening the stakes.
"What we worry about all the time in the fungal world, is fungi’s potential to cause human disease," Tom Chiller, a medical epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), told NatGeo. "There’s a lot of stuff out there we don’t even understand."
Fungi can evolve at extremely fast rates, turning into infections that are increasingly difficult to treat with antifungals. They can also force the immune system to turn against itself, a life-threatening condition known as sepsis. In a particularly alarming detail, the magazine even reported that fungi can form balls inside the body that can displace entire organs.
According to the report, mortality rates shoot up by 25 percent in the case of antifungal-resistant pathogens. The use of fungicides in the agricultural industry, for instance, allows resistant fungi to grow stronger and develop potentially dangerous immunities.
While they mutate more slowly than bacteria or viruses, generally speaking, fungi can adapt and reproduce in a great range of environments.
And that's bad news if they were ever to start spreading rapidly in humans.
"Maybe resistance to one fungicide develops in one individual and resistance to another fungicide develops in another," Marin Brewer, a plant pathologist at the University of Georgia, told NatGeo. "They can bring those resistances together through sexual reproduction and then it can explode."
Climate change could even be adding to the problem, making temperatures friendly to dangerous fungi.
In short, fungi should almost certainly be on the list of potential threats when it comes to mass outbreaks of human pathogens.
That's why experts are calling for additional funding to study fungal pathogens. Scientists are already working on developing fungal vaccines, some of which are already being tested in clinical trials.
Fungi are some of the most ubiquitous organisms on the planet — and in fact, many have proven to be incredibly useful to us. But under the right conditions, they could turn against us in an alarmingly short period of time.
So maybe it's best to get ahead of the problem now, before it's too late.
READ MORE: Humans are not prepared for a pandemic caused by fungal infections [National Geographic]
More on fungi: Scientist Says Mushrooms Have a Language They Use to Talk to Each Other
https://www.science.org/content/article/common-fungus-emerges-threat-hospitalized-covid-19-patients
Common fungus emerges as threat to hospitalized COVID-19 patients
SARS-CoV-2 and its treatments may turn the normally harmless Aspergillus fungus deadly
Science's COVID-19 reporting is supported by the Heising-Simons Foundation.
COVID-19 brings thousands of people into hospitals every day—but their coronavirus infections are not always the direct reason they die. Dangerous secondary infections by opportunistic pathogens are common in intensive care units, and physicians are raising the alarm about a particular microbial threat to COVID-19 patients: a common fungus known as Aspergillus.
Emerging evidence suggests that infection with SARS-CoV-2—and possibly the drugs used to treat it—makes COVID-19 patients especially vulnerable to Aspergillus. The threat, which also surfaced during the 2009 flu pandemic, is leading some researchers to urge more careful fungal surveillance of the sickest COVID-19 patients and treatment with antifungal drugs.
Aspergillus "is ubiquitous—you can't avoid it," says George Thompson, an infectious disease physician at the University of California, Davis. Members of its genus produce spores that can float in the air, and "we breathe in hundreds to thousands or more [of them] per day," he says.
Those spores normally don't harm us. Aspergillus infections were typically considered a threat only to immunocompromised patients, such as those undergoing cancer treatments or bone marrow transplants. But in 2009, doctors saw a spike in previously healthy people who succumbed to Aspergillus. They had all first become sick with a new, pandemic strain of the influenza virus H1N1.
For reasons scientists still don't completely understand, influenza infections appear to make the fungus more deadly in people with a seemingly normal immune system. In a 2016 review of 57 cases of Aspergillus infections in influenza patients reported since 1963, Nancy Crum-Cianflone, an infectious disease specialist at Scripps Mercy Hospital, found that about half of the co-infected patients died.
Now, something similar may be happening with COVID-19. Just as H1N1 was a severe strain of influenza, the SARS-CoV-2 virus is an especially dangerous form of coronavirus, Crum-Cianflone says. That could help explain why it leaves COVID-19 patients vulnerable to new threats.
Data on Aspergillus infections in people with COVID-19 are still sparse, but case reports point to worrying trends. One study from Germany found that one-quarter of critically ill COVID-19 patients also had Aspergillus infections. Another study of COVID-19 patients on ventilators found probable Aspergillus in one-third of them.
It's not uncommon for COVID-19 patients to be infected with other harmful microbes. But Aspergillus may be the deadliest threat among them, says Adilia Warris, a medical mycologist at the University of Exeter. She points to a recent study of 186 COVID-19 patients from around the world who also had Aspergillus. It found that slightly more than 50% of them died, and roughly one-third of those deaths were linked to Aspergillus infections.
Thompson estimates that anywhere between 2% and 10% of severely ill COVID-19 patients at his hospital also have an Aspergillus infection. "It's obviously a minority of patients," he says. "But the complications of a secondary infection are generally pretty substantial."
Doctors say there are a few reasons why having COVID-19 might be an especially strong risk factor for an Aspergillus infection. One is that while COVID-19 can send parts of the immune system into overdrive, it also depletes certain immune cells, leaving a patient less able to fight off other infections. The extreme damage to cells lining the lung also impairs the organ's ability to clear out respiratory pathogens like Aspergillus, Thompson says.
The way physicians treat COVID-19 could also heighten the risk of an Aspergillus infection. The steroid dexamethasone, shown to improve survival rates among severely ill COVID-19 patients, calms an overactive immune response that can lead to dangerous inflammation and organ damage. But immunosuppressive steroids are a double-edged sword, Crum-Cianflone says, leaving the door open to other infections. A recent observational study of four COVID-19 patients with likely Aspergillus infections noted that three of them had received higher steroid doses than was recommended—all of them died.
If doctors could easily identify Aspergillus infections, available antifungal drugs could fight them. But because the fungus can cause nonspecific symptoms such as coughing and shortness of breath that are already common in COVID-19 patients, doctors don't always look for it. A bronchoscopy, in which doctors snake a tube from the nose or mouth into the lungs, is the best way of taking lung samples for analysis. But the procedure isn't typically done on COVID-19 patients for fear of spreading viral particles. And even a positive test may not mean the fungus is doing damage; Aspergillus can also be present in the lungs as a harmless colonizer.
As a preventive measure, Crum-Cianflone has begun giving severely ill COVID-19 patients antifungal drugs after their third week of hospitalization, even if they haven't tested positive for Aspergillus. But even that strategy has risks. Overusing these compounds could lead to drug-resistant strains of Aspergillus becoming more common, Warris notes.
Recently, in The Lancet, an international group of physicians and medical mycology societies laid out recommendations for diagnosing Aspergillus infections in COVID-19 patients, including doing lung imaging scans and taking samples from the lungs at regular interval for testing. The hope is that the guidelines will help COVID-19 doctors know whether they're battling one deadly pathogen, or two.
doi: 10.1126/science.abi6454 |
| Spores of the fungus Aspergillus can be deadly if they enter the lungs of a person with a compromised immune system—or a COVID-19 infection.DAVID SCHARF/SCIENCE SOURCE |
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/deadly-fungi-are-the-newest-emerging-microbe-threat-all-over-the-world/
Deadly Fungi Are the Newest Emerging Microbe Threat All Over the World
These pathogens already kill 1.6 million people every year, and we have few defenses against them
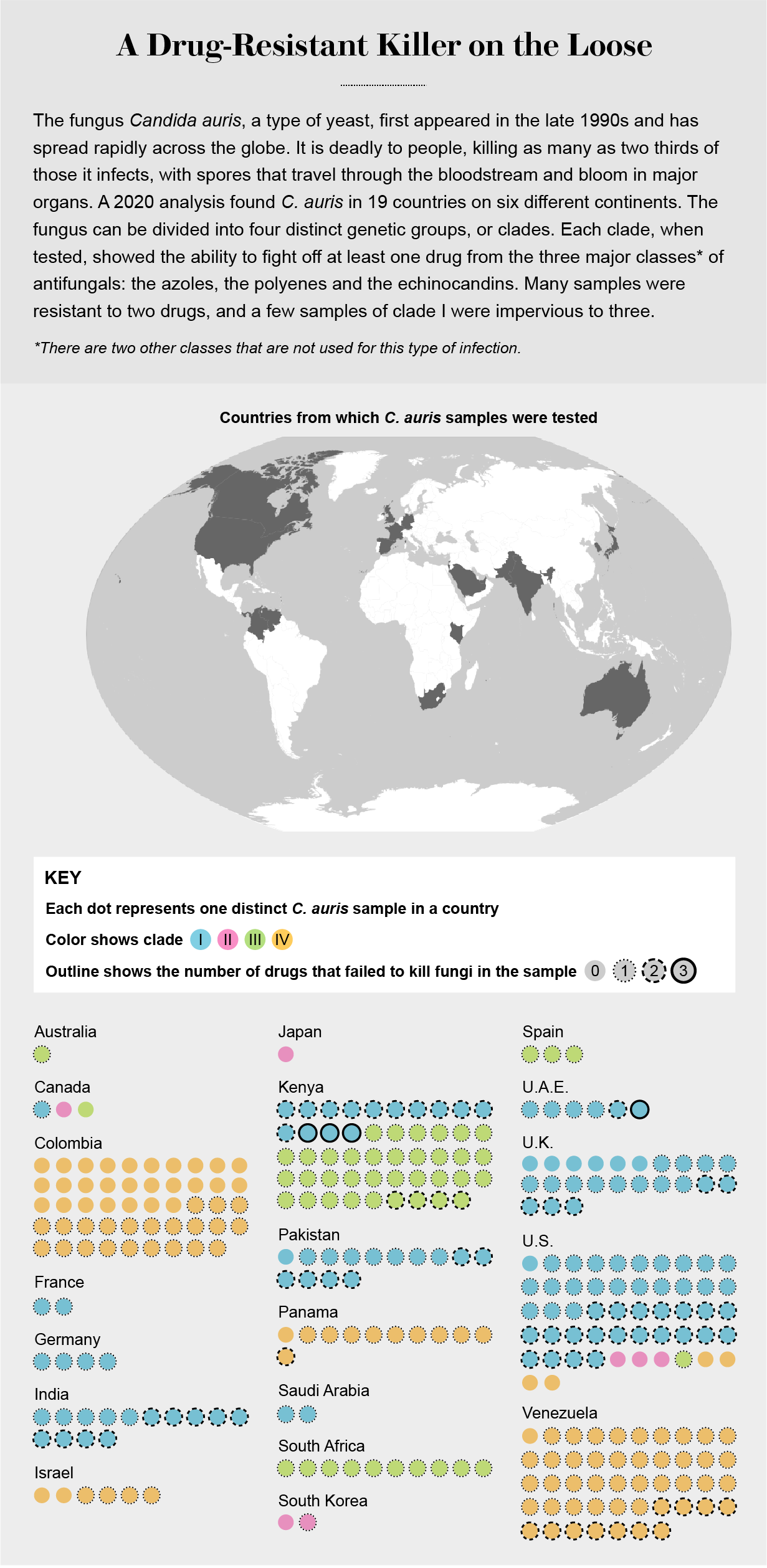
Editor’s Note (3/21/23): The dangerous fungus Candida auris is spreading rapidly in hospitals and other health care facilities, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention warned on Monday. Our June 2021 feature story, republished here, explains why C. auris can be so lethal and who is most at risk. It also describes why this pathogen and other deadly fungi are spreading throughout the world.
It was the fourth week of June in 2020, and the middle of the second wave of the COVID pandemic in the U.S. Cases had passed 2.4 million; deaths from the novel coronavirus were closing in on 125,000. In his home office in Atlanta, Tom Chiller looked up from his e-mails and scrubbed his hands over his face and shaved head.
Chiller is a physician and an epidemiologist and, in normal times, a branch chief at the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in charge of the section that monitors health threats from fungi such as molds and yeasts. He had put that specialty aside in March when the U.S. began to recognize the size of the threat from the new virus, when New York City went into lockdown and the CDC told almost all of its thousands of employees to work from home. Ever since, Chiller had been part of the public health agency's frustrating, stymied effort against COVID. Its employees had been working with state health departments, keeping tabs on reports of cases and deaths and what jurisdictions needed to do to stay safe.
Shrugging off exhaustion, Chiller focused on his in-box again. Buried in it was a bulletin forwarded by one of his staff that made him sit up and grit his teeth. Hospitals near Los Angeles that were handling an onslaught of COVID were reporting a new problem: Some of their patients had developed additional infections, with a fungus called Candida auris. The state had gone on high alert.
Chiller knew all about C. auris—possibly more about it than anyone else in the U.S. Almost exactly four years earlier he and the CDC had sent an urgent bulletin to hospitals, telling them to be on the lookout. The fungus had not yet appeared in the U.S., but Chiller had been chatting with peers in other countries and had heard what happened when the microbe invaded their health-care systems. It resisted treatment by most of the few drugs that could be used against it. It thrived on cold hard surfaces and laughed at cleaning chemicals; some hospitals where it landed had to rip out equipment and walls to defeat it. It caused fast-spreading outbreaks and killed up to two thirds of the people who contracted it.
Shortly after that warning, C. auris did enter the U.S. Before the end of 2016, 14 people contracted it, and four died. Since then, the CDC had been tracking its movement, classifying it as one of a small number of dangerous diseases that doctors and health departments had to tell the agency about. By the end of 2020 there had been more than 1,500 cases in the U.S., in 23 states. And then COVID arrived, killing people, overwhelming hospitals, and redirecting all public health efforts toward the new virus and away from other rogue organisms.
But from the start of the pandemic, Chiller had felt uneasy about its possible intersection with fungal infections. The first COVID case reports, published by Chinese scientists in international journals, described patients as catastrophically ill and consigned to intensive care: pharmaceutically paralyzed, plugged into ventilators, threaded with I.V. lines, loaded with drugs to suppress infection and inflammation. Those frantic interventions might save them from the virus—but immune-damping drugs would disable their innate defenses, and broad-spectrum antibiotics would kill off beneficial bacteria that keep invading microbes in check. Patients would be left extraordinarily vulnerable to any other pathogen that might be lurking nearby.
Chiller and his colleagues began quietly reaching out to colleagues in the U.S. and Europe, asking for any warning signs that COVID was allowing deadly fungi a foothold. Accounts of infections trickled back from India, Italy, Colombia, Germany, Austria, Belgium, Ireland, the Netherlands and France. Now the same deadly fungi were surfacing in American patients as well: the first signs of a second epidemic, layered on top of the viral pandemic. And it wasn't just C. auris. Another deadly fungus called Aspergillus was starting to take a toll as well.
“This is going to be widespread everywhere,” Chiller says. “We don't think we're going to be able to contain this.”
We are likely to think of fungi, if we think of them at all, as minor nuisances: mold on cheese, mildew on shoes shoved to the back of the closet, mushrooms springing up in the garden after hard rains. We notice them, and then we scrape them off or dust them away, never perceiving that we are engaging with the fragile fringes of a web that knits the planet together. Fungi constitute their own biological kingdom of about six million diverse species, ranging from common companions such as baking yeast to wild exotics. They differ from the other kingdoms in complex ways. Unlike animals, they have cell walls; unlike plants, they cannot make their own food; unlike bacteria, they hold their DNA within a nucleus and pack cells with organelles—features that make them, at the cellular level, weirdly similar to us.* Fungi break rocks, nourish plants, seed clouds, cloak our skin and pack our guts, a mostly hidden and unrecorded world living alongside us and within us.

That mutual coexistence is now tipping out of balance. Fungi are surging beyond the climate zones they long lived in, adapting to environments that would once have been inimical, learning new behaviors that let them leap between species in novel ways. While executing those maneuvers, they are becoming more successful pathogens, threatening human health in ways—and numbers—they could not achieve before.
Surveillance that identifies serious fungal infections is patchy, and so any number is probably an undercount. But one widely shared estimate proposes that there are possibly 300 million people infected with fungal diseases worldwide and 1.6 million deaths every year—more than malaria, as many as tuberculosis. Just in the U.S., the CDC estimates that more than 75,000 people are hospitalized annually for a fungal infection, and another 8.9 million people seek an outpatient visit, costing about $7.2 billion a year.
For physicians and epidemiologists, this is surprising and unnerving. Long-standing medical doctrine holds that we are protected from fungi not just by layered immune defenses but because we are mammals, with core temperatures higher than fungi prefer. The cooler outer surfaces of our bodies are at risk of minor assaults—think of athlete's foot, yeast infections, ringworm—but in people with healthy immune systems, invasive infections have been rare.
That may have left us overconfident. “We have an enormous blind spot,” says Arturo Casadevall, a physician and molecular microbiologist at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. “Walk into the street and ask people what are they afraid of, and they'll tell you they're afraid of bacteria, they're afraid of viruses, but they don't fear dying of fungi.”
Ironically, it is our successes that made us vulnerable. Fungi exploit damaged immune systems, but before the mid-20th century people with impaired immunity didn't live very long. Since then, medicine has gotten very good at keeping such people alive, even though their immune systems are compromised by illness or cancer treatment or age. It has also developed an array of therapies that deliberately suppress immunity, to keep transplant recipients healthy and treat autoimmune disorders such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. So vast numbers of people are living now who are especially vulnerable to fungi. (It was a fungal infection, Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, that alerted doctors to the first known cases of HIV 40 years ago this June.)
Not all of our vulnerability is the fault of medicine preserving life so successfully. Other human actions have opened more doors between the fungal world and our own. We clear land for crops and settlement and perturb what were stable balances between fungi and their hosts. We carry goods and animals across the world, and fungi hitchhike on them. We drench crops in fungicides and enhance the resistance of organisms residing nearby. We take actions that warm the climate, and fungi adapt, narrowing the gap between their preferred temperature and ours that protected us for so long.
But fungi did not rampage onto our turf from some foreign place. They were always with us, woven through our lives and our environments and even our bodies: every day, every person on the planet inhales at least 1,000 fungal spores. It is not possible to close ourselves off from the fungal kingdom. But scientists are urgently trying to understand the myriad ways in which we dismantled our defenses against the microbes, to figure out better approaches to rebuild them.
It is perplexing that we humans have felt so safe from fungi when we have known for centuries that our crops can be devastated from their attacks. In the 1840s a funguslike organism, Phytophthora infestans, destroyed the Irish potato crop; more than one million people, one eighth of the population, starved to death. (The microbe, formerly considered a fungus, is now classified as a highly similar organism, a water mold.) In the 1870s coffee leaf rust, Hemileia vastatrix, wiped out coffee plants in all of South Asia, completely reordering the colonial agriculture of India and Sri Lanka and transferring coffee production to Central and South America. Fungi are the reason that billions of American chestnut trees vanished from Appalachian forests in the U.S. in the 1920s and that millions of dying Dutch elms were cut out of American cities in the 1940s. They destroy one fifth of the world's food crops in the field every year.
Yet for years medicine looked at the devastation fungi wreak on the plant kingdom and never considered that humans or other animals might be equally at risk. “Plant pathologists and farmers take fungi very seriously and always have, and agribusiness has,” says Matthew C. Fisher, a professor of epidemiology at Imperial College London, whose work focuses on identifying emerging fungal threats. “But they're very neglected from the point of view of wildlife disease and also human disease.”
So when the feral cats of Rio de Janeiro began to fall ill, no one at first thought to ask why. Street cats have hard lives anyway, scrounging, fighting and birthing endless litters of kittens. But in the summer of 1998, dozens and then hundreds of neighborhood cats began showing horrific injuries: weeping sores on their paws and ears, clouded swollen eyes, what looked like tumors blooming out of their faces. The cats of Rio live intermingled with humans: Children play with them, and especially in poor neighborhoods women encourage them to stay near houses and deal with rats and mice. Before long some of the kids and mothers started to get sick as well. Round, crusty-edge wounds opened on their hands, and hard red lumps trailed up their arms as though following a track.
In 2001 researchers at the Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, a hospital and research institute located in Rio, realized they had treated 178 people in three years, mostly mothers and grandmothers, for similar lumps and oozing lesions. Almost all of them had everyday contact with cats. Analyzing the infections and ones in cats treated at a nearby vet clinic, they found a fungus called Sporothrix.
The various species of the genus Sporothrix live in soil and on plants. Introduced into the body by a cut or scratch, this fungus transforms into a budding form resembling a yeast. In the past, the yeast form had not been communicable, but in this epidemic, it was. That was how the cats were infecting one another and their caretakers: Yeasts in their wounds and saliva flew from cat to cat when they fought or jostled or sneezed. Cats passed it to humans via claws and teeth and caresses. The infections spread from skin up into lymph nodes and the bloodstream and to eyes and internal organs. In case reports amassed by doctors in Brazil, there were accounts of fungal cysts growing in people's brains.
The fungus with this skill was decreed a new species, Sporothrix brasiliensis. By 2004, 759 people had been treated for the disease at the Cruz Foundation; by 2011, the count was up to 4,100 people. By last year, more than 12,000 people in Brazil had been diagnosed with the disease across a swath of more than 2,500 miles. It has spread to Paraguay, Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia and Panama.
“This epidemic will not take a break,” says Flávio Queiroz-Telles, a physician and associate professor at the Federal University of Paraná in Curitiba, who saw his first case in 2011. “It is expanding.”
“This epidemic will not take a break,” says Flávio Queiroz-Telles, a physician and associate professor at the Federal University of Paraná in Curitiba, who saw his first case in 2011. “It is expanding.”
It was a mystery how: Feral cats wander, but they do not migrate thousands of miles. At the CDC, Chiller and his colleagues suspected a possible answer. In Brazil and Argentina, sporotrichosis has been found in rats as well as cats. Infected rodents could hop rides on goods that move into shipping containers. Millions of those containers land on ships docking at American ports every day. The fungus could be coming to the U.S. A sick rat that escaped a container could seed the infection in the city surrounding a port.
“In dense population centers, where a lot of feral cats are, you could see an increase in extremely ill cats that are roaming the streets,” says John Rossow, a veterinarian at the CDC, who may have been the first to notice the possible threat of Sporothrix to the U.S. “And being that we Americans can't avoid helping stray animals, I imagine we're going to see a lot of transmission to people.”
To a mycologist such as Chiller, this kind of spread is a warning: The fungal kingdom is on the move, pressing against the boundaries, seeking any possible advantage in its search for new hosts. And that we, perhaps, are helping them. “Fungi are alive; they adapt,” he says. Among their several million species, “only around 300 that we know of cause human disease—so far. That's a lot of potential for newness and differentness, in things that have been around for a billion years.”
Torrence Irvin was 44 years old when his fungal troubles started. A big healthy man who had been an athlete in high school and college, he lives in Patterson, Calif., a quiet town in the Central Valley tucked up against U.S. Route 5. A little more than two years earlier Irvin had bought a house in a new subdivision and moved in with his wife, Rhonda, and their two daughters. He was a warehouse manager for the retailer Crate & Barrel and the announcer for local youth football games.
In September 2018 Irvin started to feel like he had picked up a cold he couldn't shake. He dosed himself with Nyquil, but as the weeks went on, he felt weak and short of breath. On a day in October, he collapsed, falling to his knees in his bedroom. His daughter found him. His wife insisted they go to the emergency room.
Doctors thought he had pneumonia. They sent him home with antibiotics and instructions to use over-the-counter drugs. He got weaker and couldn't keep food down. He went to other doctors, while steadily getting worse, enduring shortness of breath, night sweats, and weight loss similar to a cancer victim's. From 280 pounds, he shrank to 150. Eventually one test turned up an answer: a fungal infection called coccidioidomycosis, usually known as Valley fever. “Until I got it, I had never heard of it,” he says.
But others had. Irvin was referred to the University of California, Davis, 100 miles from his house, which had established a Center for Valley Fever. The ailment occurs mostly in California and Arizona, the southern tip of Nevada, New Mexico and far west Texas. The microbes behind it, Coccidioides immitis and Coccidioides posadasii, infect about 150,000 people in that area every year—and outside of the region the infection is barely known. “It's not a national pathogen—you don't get it in densely populated New York or Boston or D.C.,” says George R. Thompson, co-director of the Davis center and the physician who began to supervise Irvin's care. “So even physicians view it as some exotic disease. But in areas where it's endemic, it's very common.”
Similar to Sporothrix, Coccidioides has two forms, starting with a thready, fragile one that exists in soil and breaks apart when soil is disturbed. Its lightweight components can blow on the wind for hundreds of miles. Somewhere in his life in the Central Valley, Irvin had inhaled a dose. The fungus had transformed in his body into spheres packed with spores that migrated via his blood, infiltrating his skull and spine. To protect him, his body produced scar tissue that stiffened and blocked off his lungs. By the time he came under Thompson's care, seven months after he first collapsed, he was breathing with just 25 percent of his lung capacity. As life-threatening as that was, Irvin was nonetheless lucky: in about one case out of 100, the fungus grows life-threatening masses in organs and the membranes around the brain.
Irvin had been through all the approved treatments. There are only five classes of antifungal drugs, a small number compared with the more than 20 classes of antibiotics to fight bacteria. Antifungal medications are so few in part because they are difficult to design: because fungi and humans are similar at the cellular level, it is challenging to create a drug that can kill them without killing us, too.
It is so challenging that a new class of antifungals reaches the market only every 20 years or so: the polyene class, including amphotericin B, in the 1950s; the azoles in the 1980s; and the echinocandin drugs, the newest remedy, beginning in 2001. (There is also terbinafine, used mostly for external infections, and flucytosine, used mostly in combination with other drugs.)
For Irvin, nothing worked well enough. “I was a skeleton,” he recalls. “My dad would come visit and sit there with tears in his eyes. My kids didn't want to see me.”
In a last-ditch effort, the Davis team got Irvin a new drug called olorofim. It is made in the U.K. and is not yet on the market, but a clinical trial was open to patients for whom every other drug had failed. Irvin qualified. Almost as soon as he received it, he began to turn the corner. His cheeks filled out. He levered himself to his feet with a walker. In several weeks, he went home.
Valley fever is eight times more common now than it was 20 years ago. That period coincides with more migration to the Southwest and West Coast—more house construction, more stirring up of soil—and also with increases in hot, dry weather linked to climate change. “Coccidioides is really happy in wet soil; it doesn't form spores, and thus it isn't particularly infectious,” Thompson says. “During periods of drought, that's when the spores form. And we've had an awful lot of drought in the past decade.”
Because Valley fever has always been a desert malady, scientists assumed the fungal threat would stay in those areas. But that is changing. In 2010 three people came down with Valley fever in eastern Washington State, 900 miles to the north: a 12-year-old who had been playing in a canyon and breathed the spores in, a 15-year-old who fell off an ATV and contracted Valley fever through his wounds, and a 58-year-old construction worker whose infection went to his brain. Research published two years ago shows such cases might become routine. Morgan Gorris, an earth systems scientist at Los Alamos National Laboratory, used climate-warming scenarios to project how much of the U.S. might become friendly territory for Coccidioides by the end of this century. In the scenario with the highest temperature rise, the area with conditions conducive to Valley fever—a mean annual temperature of 10.7 degrees Celsius (51 degrees Fahrenheit) and mean annual rainfall of less than 600 millimeters (23.6 inches)—reaches to the Canadian border and covers most of the western U.S.
Irvin has spent almost two years recovering; he still takes six pills of olorifim a day and expects to do that indefinitely. He gained back weight and strength, but his lungs remain damaged, and he has had to go on disability. “I am learning to live with this,” he says. “I will be dealing with it for the rest of my life.”
.jpg)
Sporothrix found a new way to transmit itself. Valley fever expanded into a new range. C. auris, the fungus that took advantage of COVID, performed a similar trick, exploiting niches opened by the chaos of the pandemic.
That fungus was already a bad actor. It did not behave the way that other pathogenic yeasts do, living quiescently in someone's gut and surging out into their blood or onto mucous membranes when their immune system shifted out of balance. At some point in the first decade of the century, C. auris gained the ability to directly pass from person to person. It learned to live on metal, plastic, and the rough surfaces of fabric and paper. When the first onslaught of COVID created a shortage of disposable masks and gowns, it forced health-care workers to reuse gear they usually discard between patients, to keep from carrying infections. And C. auris was ready.
In New Delhi, physician and microbiologist Anuradha Chowdhary read the early case reports and was unnerved that COVID seemed to be an inflammatory disease as much as a respiratory one. The routine medical response to inflammation would be to damp down the patient's immune response, using steroids. That would set patients up to be invaded by fungi, she realized. C. auris, lethal and persistent, had already been identified in hospitals in 40 countries on every continent except Antarctica. If health-care workers unknowingly carried the organism through their hospitals on reused clothing, there would be a conflagration.
“I thought, ‘Oh, God, I.C.U.s are going to be overloaded with patients, and infection-control policies are going to be compromised,'” she said recently. “In any I.C.U. where C. auris is already present, it is going to play havoc.”
Chowdhary published a warning to other physicians in a medical journal early in the pandemic. Within a few months she wrote an update: a 65-bed I.C.U. in New Delhi had been invaded by C. auris, and two thirds of the patients who contracted the yeast after they were admitted with COVID died. In the U.S., the bulletin that Chiller received flagged several hundred cases in hospitals and long-term care facilities in Los Angeles and nearby Orange County, and a single hospital in Florida disclosed that it harbored 35. Where there were a few, the CDC assumed that there were more—but that routine testing, their keyhole view into the organism's stealthy spread, had been abandoned under the overwork of caring for pandemic patients.
As bad as that was, physicians familiar with fungi were watching for a bigger threat: the amplification of another fungus that COVID might give an advantage to.
In nature, Aspergillus fumigatus serves as a clean-up crew. It encourages the decay of vegetation, keeping the world from being submerged in dead plants and autumn leaves. Yet in medicine, Aspergillus is known as the cause of an opportunistic infection spawned when a compromised human immune system cannot sweep away its spores. In people who are already ill, the mortality rate of invasive aspergillosis hovers near 100 percent.
During the 2009 pandemic of H1N1 avian flu, Aspergillus began finding new victims, healthy people whose only underlying illness was influenza. In hospitals in the Netherlands, a string of flu patients arrived unable to breathe and going into shock. In days, they died. By 2018 what physicians were calling invasive pulmonary aspergillosis was occurring in one out of three patients critically ill with flu and killing up to two thirds of them.
Then the coronavirus arrived. It scoured the interior lung surface the way flu does. Warning networks that link infectious disease doctors and mycologists around the globe lit up with accounts of aspergillosis taking down patients afflicted with COVID: in China, France, Belgium, Germany, the Netherlands, Austria, Ireland, Italy and Iran. As challenging a complication as C. auris was, Aspergillus was worse. C. auris lurks in hospitals. The place where patients were exposed to Aspergillus was, well, everywhere. There was no way to eliminate the spores from the environment or keep people from breathing them in.
In Baltimore, physician Kieren Marr was acutely aware of the danger. Marr is a professor of medicine and oncology at Johns Hopkins Medical Center and directs its unit on transplant and oncology infectious diseases. The infections that take hold in people who have received a new organ or gotten a bone marrow transplant are familiar territory for her. When COVID arrived, she was concerned that Aspergillus would surge—and that U.S. hospitals, not alert to the threat, would miss it. Johns Hopkins began testing COVID patients in its I.C.U. with the kind of molecular diagnostic tests used in Europe, trying to catch up to the infection in time to try to treat it. Across the five hospitals the Johns Hopkins system operates, it found that one out of 10 people with severe COVID was developing aspergillosis.
Several patients died, including one whose aspergillosis went to the brain. Marr feared there were many others like that patient, across the country, whose illness was not being detected in time. “This is bad,” Marr said this spring. “Aspergillus is more important in COVID right now than C. auris. Without a doubt.”
The challenge of countering pathogenic fungi is not only that they are virulent and sneaky, as bad as those traits may be. It is that fungi have gotten very good at protecting themselves against drugs we use to try to kill them.
The story is similar to that of antibiotic resistance. Drugmakers play a game of leapfrog, trying to get in front of the evolutionary maneuvers that bacteria use to protect themselves from drugs. For fungi, the tale is the same but worse. Fungal pathogens gain resistance against antifungal agents—but there are fewer drugs to start with, because the threat was recognized relatively recently.
“In the early 2000s, when I moved from academia to industry, the antifungal pipeline was zero,” says John H. Rex, a physician and longtime advocate for antibiotic development. Rex is chief medical officer of F2G, which makes the not yet approved drug that Torrence Irvin took. “There were no antifungals anywhere in the world in clinical or even preclinical development.”
That is no longer the case, but research is slow; as with antibiotics, the financial rewards of bringing a new drug to market are uncertain. But developing new drugs is critical because patients may need to take them for months, sometimes for years, and many of the existing antifungals are toxic to us. (Amphotericin B gets called “shake and bake” for its grueling side effects.) “As a physician, you're making a choice to deal with a fungal infection at the cost of the kidney,” says Ciara Kennedy, president and CEO of Amplyx Pharmaceuticals, which has a novel antifungal under development. “Or if I don't deal with the fungal infection, knowing the patient's going to die.”
Developing new drugs also is critical because the existing ones are losing their effectiveness. Irvin ended up in the olorofim trial because his Valley fever did not respond to any available drugs. C. auris already shows resistance to drugs in all three major antifungal classes. Aspergillus has been amassing resistance to the antifungal group most useful for treating it, known as the azoles, because it is exposed to them so persistently. Azoles are used all across the world—not only in agriculture to control crop diseases but in paints and plastics and building materials. In the game of leapfrog, fungi are already in front.
The best counter to the ravages of fungi is not treatment but prevention: not drugs but vaccines. Right now no vaccine exists for any fungal disease. But the difficulty of treating patients long term with toxic drugs, combined with staggering case numbers, makes finding one urgent. And for the first time, one might be in sight if not in reach.
The reason that rates of Valley fever are not worse than they are, when 10 percent of the U.S. population lives in the endemic area, is that infection confers lifelong immunity. That suggests a vaccine might be possible—and since the 1940s researchers have been trying. A prototype that used a killed version of the form Coccidioides takes inside the body—fungal spheres packed with spores—worked brilliantly in mice. But it failed dismally in humans in a clinical trial in the 1980s.
“We did it on a shoestring, and everyone wanted it to work,” says John Galgiani, now a professor and director of the Valley Fever Center for Excellence at the University of Arizona College of Medicine, who was part of that research 40 years ago. “Even with [bad] reactions and the study lasting three years, we kept 95 percent of the people who enrolled.”
Enter dogs. They have their noses in the dirt all the time, and that puts them at more at risk of Valley fever than humans are. In several Arizona counties, close to 10 percent of dogs come down with the disease every year, and they are more likely to develop severe lung-blocking forms than human are. They suffer terribly, and it is lengthy and expensive to treat them. But dogs' vulnerability—plus the lower standards that federal agencies require to approve animal drugs compared with human ones—makes them a model system for testing a possible vaccine. And the passion of owners for their animals and their willingness to empty their wallets when they can may turn possibility into reality for the first time.
Galgiani and his Arizona group are now working on a new vaccine formula, thanks to financial donations from hundreds of dog owners, plus a boost from a National Institutes of Health grant and commercial assistance from a California company, Anivive Lifesciences. Testing is not complete, but it could reach the market for use in dogs as early as next year. “I think this is proof of concept for a fungal vaccine—having it in use in dogs, seeing it is safe,” says Lisa Shubitz, a veterinarian and research scientist at the Arizona center. “I really believe this is the path to a human vaccine.”
This injection does not depend on a killed Valley fever fungus. Instead it uses a live version of the fungus from which a gene that is key to its reproductive cycle, CPS1, has been deleted. The loss means the fungi are unable to spread. The gene was discovered by a team of plant pathologists and later was identified in Coccidioides by Marc Orbach of the University of Arizona, who studies host-pathogen interactions. After creating a mutant Coccidioides with the gene removed, he and Galgiani experimentally infected lab mice bred to be exquisitely sensitive to the fungus. The microbe provoked a strong immune reaction, activating type 1 T helper cells, which establish durable immunity. The mice survived for six months and did not develop any Valley fever symptoms, even though the team tried to infect them with unaltered Coccidioides. When the researchers autopsied the mice at the end of that half-year period, scientists found almost no fungus growing in their lungs. That long-lasting protection against infection makes the gene-deleted fungus the most promising basis for a vaccine since Galgiani's work in the 1980s. But turning a vaccine developed for dogs into one that could be used in humans will not be quick.
The canine formula comes under the purview of the U.S. Department of Agriculture, but approval of a human version would be overseen by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. It would require clinical trials that would probably stretch over years and involve thousands of people rather than the small number of animals used to validate the formula in dogs. Unlike the 1980s prototype, the new vaccine involves a live organism. Because there has never been a fungal vaccine approved, there is no preestablished evaluation pathway for the developers or regulatory agencies to follow. “We would be flying the plane and building it at the same time,” Galgiani says.
He estimates achieving a Valley fever vaccine for people could take five to seven years and about $150 million, an investment made against an uncertain promise of earnings. But a successful compound could have broad usefulness, protecting permanent residents of the Southwest as well as the military personnel at 120 bases and other installations in the endemic area, plus hundreds of thousands of “snowbird” migrants who visit every winter. (Three years ago the CDC identified cases of Valley fever in 14 states outside the endemic zone. Most were in wintertime inhabitants of the Southwest who were diagnosed after they went back home.) By one estimate, a vaccine could save potentially $1.5 billion in health-care costs every year.
“I couldn't see the possibility that we'd have a vaccine 10 years ago,” Galgiani says. “But I think it is possible now.”
If one fungal vaccine is achieved, it would carve the path for another. If immunizations were successful—scientifically, as targets of regulation and as vaccines people would be willing to accept—we would no longer need to be on constant guard against the fungal kingdom. We could live alongside and within it, safely and confidently, without fear of the ravages it can wreak.
But that is years away, and fungi are moving right now: changing their habits, altering their patterns, taking advantage of emergencies such as COVID to find fresh victims. At the CDC, Chiller is apprehensive.
“The past five years really felt like we were waking up to a whole new phenomenon, a fungal world that we just weren't used to,” Chiller says. “How do we stay on top of that? How do we question ourselves to look for what might come next? We study these emergences not as an academic exercise but because they show us what might be coming. We need to be prepared for more surprises.”
*Editor’s Note (6/9/21): This sentence was revised after posting to correct the description of how the cells of fungi differ from those of animals.
This article was originally published with the title "Deadly Kingdom" in Scientific American 324, 6, 26-35 (June 2021)
doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0621-26
 |
| Fungus Candida auris lurks in hospitals, where it infects patients with impaired immune systems. Credit: Juan Gaertner Science Source |
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
- Bloggery committed by chris tower - 2306.24 - 10:10
- Days ago = 2913 days ago

No comments:
Post a Comment